#include <fem_physics.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| FEMPhysics () | |
| virtual | ~FEMPhysics () |
| virtual bool | eulerian_residual (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &context) override |
| virtual bool | mass_residual (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) override |
| virtual std::unique_ptr< DifferentiablePhysics > | clone_physics ()=0 |
| virtual void | clear_physics () |
| virtual void | init_physics (const System &sys) |
| virtual bool | element_time_derivative (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual bool | element_constraint (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual bool | side_time_derivative (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual bool | side_constraint (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual bool | nonlocal_time_derivative (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual bool | nonlocal_constraint (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual void | time_evolving (unsigned int var) |
| virtual void | time_evolving (unsigned int var, unsigned int order) |
| bool | is_time_evolving (unsigned int var) const |
| virtual bool | side_mass_residual (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual bool | nonlocal_mass_residual (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &c) |
| virtual bool | damping_residual (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual bool | side_damping_residual (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual bool | nonlocal_damping_residual (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| virtual void | init_context (DiffContext &) |
| virtual void | set_mesh_system (System *sys) |
| const System * | get_mesh_system () const |
| System * | get_mesh_system () |
| virtual void | set_mesh_x_var (unsigned int var) |
| unsigned int | get_mesh_x_var () const |
| virtual void | set_mesh_y_var (unsigned int var) |
| unsigned int | get_mesh_y_var () const |
| virtual void | set_mesh_z_var (unsigned int var) |
| unsigned int | get_mesh_z_var () const |
| bool | _eulerian_time_deriv (bool request_jacobian, DiffContext &) |
| bool | have_first_order_vars () const |
| const std::set< unsigned int > & | get_first_order_vars () const |
| bool | is_first_order_var (unsigned int var) const |
| bool | have_second_order_vars () const |
| const std::set< unsigned int > & | get_second_order_vars () const |
| bool | is_second_order_var (unsigned int var) const |
Public Attributes | |
| bool | compute_internal_sides |
Protected Attributes | |
| System * | _mesh_sys |
| unsigned int | _mesh_x_var |
| unsigned int | _mesh_y_var |
| unsigned int | _mesh_z_var |
| std::vector< unsigned int > | _time_evolving |
| std::set< unsigned int > | _first_order_vars |
| std::set< unsigned int > | _second_order_vars |
| std::map< unsigned int, unsigned int > | _second_order_dot_vars |
Detailed Description
This class provides a specific system class. It aims to generalize any system, linear or nonlinear, which provides both a residual and a Jacobian.
This class is part of the new DifferentiableSystem framework, which is still experimental. Users of this framework should beware of bugs and future API changes.
- Date
- 2012
Definition at line 44 of file fem_physics.h.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ FEMPhysics()
|
inline |
Constructor.
Definition at line 51 of file fem_physics.h.
◆ ~FEMPhysics()
|
inlinevirtual |
Member Function Documentation
◆ _eulerian_time_deriv()
|
inherited |
This method simply combines element_time_derivative() and eulerian_residual(), which makes its address useful as a pointer-to-member-function when refactoring.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::element_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::element_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::element_residual().
◆ clear_physics()
|
virtualinherited |
Clear any data structures associated with the physics.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::clear().
◆ clone_physics()
|
pure virtualinherited |
Copy of this object. User should override to copy any needed state.
Implemented in libMesh::DifferentiableSystem.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::attach_physics().
◆ damping_residual()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Subtracts a damping vector contribution on elem from elem_residual. This method is not used in first-order-in-time problems. For second-order-in-time problems, this is the 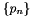 term. This method is only called for UnsteadySolver-based TimeSolvers.
term. This method is only called for UnsteadySolver-based TimeSolvers.
If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should compute elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If elem_jacobian has not been computed then the method should return false.
If the problem has no damping, the default "do-nothing" is correct. Otherwise, this must be reimplemented.
Definition at line 374 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::element_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::element_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::element_residual().
◆ element_constraint()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Adds the constraint contribution on elem to elem_residual. If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should compute elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If elem_jacobian has not been computed then the method should return false.
Users may need to reimplement this for their particular PDE.
To implement the constraint 0 = G(u), the user should examine u = elem_solution and add (G(u), phi_i) to elem_residual in elem_constraint().
Definition at line 142 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::element_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::element_residual(), libMesh::SteadySolver::element_residual(), libMesh::EigenTimeSolver::element_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::element_residual().
◆ element_time_derivative()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Adds the time derivative contribution on elem to elem_residual. If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should compute elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If elem_jacobian has not been computed then the method should return false.
Users need to reimplement this for their particular PDE.
To implement the physics model du/dt = F(u), the user should examine u = elem_solution and add (F(u), phi_i) to elem_residual in elem_time_derivative().
Definition at line 124 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::SteadySolver::element_residual(), and libMesh::EigenTimeSolver::element_residual().
◆ eulerian_residual()
|
overridevirtual |
Adds a pseudo-convection contribution on elem to elem_residual, if the nodes of elem are being translated by a moving mesh.
This function assumes that the user's time derivative equations (except for any equations involving unknown mesh xyz coordinates themselves) are expressed in an Eulerian frame of reference, and that the user is satisfied with an unstabilized convection term. Lagrangian equations will probably require overriding eulerian_residual() with a blank function; ALE or stabilized formulations will require reimplementing eulerian_residual() entirely.
Reimplemented from libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics.
◆ get_first_order_vars()
|
inlineinherited |
- Returns
- The set of first order in time variable indices. May be empty.
Definition at line 517 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_first_order_vars.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::have_first_order_scalar_vars().
◆ get_mesh_system() [1/2]
|
inlineinherited |
- Returns
- A const reference to the system with variables corresponding to mesh nodal coordinates, or nullptr if the mesh is fixed. Useful for ALE calculations.
Definition at line 624 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_mesh_sys.
Referenced by libMesh::FEMSystem::build_context().
◆ get_mesh_system() [2/2]
|
inlineinherited |
- Returns
- A reference to the system with variables corresponding to mesh nodal coordinates, or nullptr if the mesh is fixed.
Definition at line 630 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_mesh_sys.
◆ get_mesh_x_var()
|
inlineinherited |
- Returns
- The variable number corresponding to the mesh x coordinate. Useful for ALE calculations.
Definition at line 636 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_mesh_x_var.
Referenced by libMesh::FEMSystem::build_context().
◆ get_mesh_y_var()
|
inlineinherited |
- Returns
- The variable number corresponding to the mesh y coordinate. Useful for ALE calculations.
Definition at line 642 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_mesh_y_var.
Referenced by libMesh::FEMSystem::build_context().
◆ get_mesh_z_var()
|
inlineinherited |
- Returns
- The variable number corresponding to the mesh z coordinate. Useful for ALE calculations.
Definition at line 648 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_mesh_z_var.
Referenced by libMesh::FEMSystem::build_context().
◆ get_second_order_vars()
|
inlineinherited |
- Returns
- The set of second order in time variable indices. May be empty.
Definition at line 530 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_second_order_vars.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::add_second_order_dot_vars(), libMesh::DiffContext::DiffContext(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::element_residual(), libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::have_second_order_scalar_vars(), and libMesh::FEMContext::pre_fe_reinit().
◆ have_first_order_vars()
|
inlineinherited |
Definition at line 511 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_first_order_vars.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::have_first_order_scalar_vars().
◆ have_second_order_vars()
|
inlineinherited |
Definition at line 524 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_second_order_vars.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::element_residual(), and libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::have_second_order_scalar_vars().
◆ init_context()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
◆ init_physics()
|
virtualinherited |
Initialize any data structures associated with the physics.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::attach_physics(), and libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::init_data().
◆ is_first_order_var()
|
inlineinherited |
Definition at line 520 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_first_order_vars.
◆ is_second_order_var()
|
inlineinherited |
Definition at line 533 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_second_order_vars.
Referenced by libMesh::FirstOrderUnsteadySolver::compute_second_order_eqns().
◆ is_time_evolving()
|
inlineinherited |
- Returns
trueiff variablevaris evolving with respect to time. In general, the user's init() function should have set time_evolving() for any variables which behave like du/dt = F(u), and should not call time_evolving() for any variables which behave like 0 = G(u).
Definition at line 277 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_time_evolving.
Referenced by libMesh::FEMSystem::init_context().
◆ mass_residual()
|
overridevirtual |
Subtracts a mass vector contribution on elem from elem_residual.
If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should compute elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If elem_jacobian has not been computed then the method should return false.
Many problems can use the reimplementation in FEMPhysics::mass_residual which subtracts (du/dt,v) for each transient variable u; users with more complicated transient problems will need to reimplement this themselves.
Reimplemented from libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics.
◆ nonlocal_constraint()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Adds any nonlocal constraint contributions (e.g. some components of constraints in scalar variable equations) to elem_residual
If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should also modify elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If the Jacobian changes have not been computed then the method should return false.
Users may need to reimplement this for PDEs on systems to which SCALAR variables with non-transient equations have been added.
Definition at line 227 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::nonlocal_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::nonlocal_residual(), libMesh::SteadySolver::nonlocal_residual(), libMesh::EigenTimeSolver::nonlocal_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::nonlocal_residual().
◆ nonlocal_damping_residual()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Subtracts any nonlocal damping vector contributions (e.g. any first time derivative coefficients in scalar variable equations) from elem_residual
If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should also modify elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If the Jacobian changes have not been computed then the method should return false.
Definition at line 406 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::nonlocal_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::nonlocal_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::nonlocal_residual().
◆ nonlocal_mass_residual()
|
virtualinherited |
Subtracts any nonlocal mass vector contributions (e.g. any time derivative coefficients in scalar variable equations) from elem_residual
If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should also modify elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If the Jacobian changes have not been computed then the method should return false.
Many problems can use the reimplementation in FEMPhysics::mass_residual which subtracts (du/dt,v) for each transient scalar variable u; users with more complicated transient scalar variable equations will need to reimplement this themselves.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::nonlocal_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::nonlocal_residual(), libMesh::EigenTimeSolver::nonlocal_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::nonlocal_residual().
◆ nonlocal_time_derivative()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Adds any nonlocal time derivative contributions (e.g. some components of time derivatives in scalar variable equations) to elem_residual
If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should also modify elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If the Jacobian changes have not been computed then the method should return false.
Users may need to reimplement this for PDEs on systems to which SCALAR variables have been added.
Definition at line 209 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::nonlocal_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::nonlocal_residual(), libMesh::SteadySolver::nonlocal_residual(), libMesh::EigenTimeSolver::nonlocal_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::nonlocal_residual().
◆ set_mesh_system()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Tells the DifferentiablePhysics that system sys contains the isoparametric Lagrangian variables which correspond to the coordinates of mesh nodes, in problems where the mesh itself is expected to move in time.
The system with mesh coordinate data (which may be this system itself, for fully coupled moving mesh problems) is currently assumed to have new (end of time step) mesh coordinates stored in solution, old (beginning of time step) mesh coordinates stored in _old_nonlinear_solution, and constant velocity motion during each time step.
Activating this function ensures that local (but not neighbor!) element geometry is correctly repositioned when evaluating element residuals.
Currently sys must be *this for a tightly coupled moving mesh problem or nullptr to stop mesh movement; loosely coupled moving mesh problems are not implemented.
This code is experimental. "Trust but verify, and not in that order"
Definition at line 580 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_mesh_sys.
◆ set_mesh_x_var()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Tells the DifferentiablePhysics that variable var from the mesh system should be used to update the x coordinate of mesh nodes, in problems where the mesh itself is expected to move in time.
The system with mesh coordinate data (which may be this system itself, for fully coupled moving mesh problems) is currently assumed to have new (end of time step) mesh coordinates stored in solution, old (beginning of time step) mesh coordinates stored in _old_nonlinear_solution, and constant velocity motion during each time step.
Activating this function ensures that local (but not neighbor!) element geometry is correctly repositioned when evaluating element residuals.
Definition at line 600 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_mesh_x_var.
◆ set_mesh_y_var()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Tells the DifferentiablePhysics that variable var from the mesh system should be used to update the y coordinate of mesh nodes.
Definition at line 608 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_mesh_y_var.
◆ set_mesh_z_var()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Tells the DifferentiablePhysics that variable var from the mesh system should be used to update the z coordinate of mesh nodes.
Definition at line 616 of file diff_physics.h.
References libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::_mesh_z_var.
◆ side_constraint()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Adds the constraint contribution on side of elem to elem_residual. If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should compute elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If elem_jacobian has not been computed then the method should return false.
Users may need to reimplement this for their particular PDE depending on the boundary conditions.
To implement a weak form of the constraint 0 = G(u), the user should examine u = elem_solution and add (G(u), phi_i) boundary integral contributions to elem_residual in side_constraint().
Definition at line 191 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::side_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::side_residual(), libMesh::SteadySolver::side_residual(), libMesh::EigenTimeSolver::side_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::side_residual().
◆ side_damping_residual()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Subtracts a damping vector contribution on side of elem from elem_residual. If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should compute elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If elem_jacobian has not been computed then the method should return false.
For most problems, the default implementation of "do nothing" is correct; users with boundary conditions including first time derivatives may need to reimplement this themselves.
Definition at line 391 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::side_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::side_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::side_residual().
◆ side_mass_residual()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Subtracts a mass vector contribution on side of elem from elem_residual. If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should compute elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If elem_jacobian has not been computed then the method should return false.
For most problems, the default implementation of "do nothing" is correct; users with boundary conditions including time derivatives may need to reimplement this themselves.
Definition at line 335 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::side_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::side_residual(), libMesh::EigenTimeSolver::side_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::side_residual().
◆ side_time_derivative()
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Adds the time derivative contribution on side of elem to elem_residual. If this method receives request_jacobian = true, then it should compute elem_jacobian and return true if possible. If elem_jacobian has not been computed then the method should return false.
Users may need to reimplement this for their particular PDE depending on the boundary conditions.
To implement a weak form of the source term du/dt = F(u) on sides, such as might arise in a flux boundary condition, the user should examine u = elem_solution and add (F(u), phi_i) boundary integral contributions to elem_residual in side_constraint().
Definition at line 171 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::EulerSolver::side_residual(), libMesh::Euler2Solver::side_residual(), libMesh::SteadySolver::side_residual(), libMesh::EigenTimeSolver::side_residual(), and libMesh::NewmarkSolver::side_residual().
◆ time_evolving() [1/2]
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Tells the DiffSystem that variable var is evolving with respect to time. In general, the user's init() function should call time_evolving() for any variables which behave like du/dt = F(u), and should not call time_evolving() for any variables which behave like 0 = G(u).
Most derived systems will not have to reimplement this function; however any system which reimplements mass_residual() may have to reimplement time_evolving() to prepare data structures.
- Deprecated:
- Instead, use the time_evolving override and specify the order-in-time of the variable, either 1 or 2. This method assumes the variable is first order for backward compatibility.
Definition at line 249 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::add_second_order_dot_vars().
◆ time_evolving() [2/2]
|
virtualinherited |
Tells the DiffSystem that variable var is evolving with respect to time. In general, the user's init() function should call time_evolving() with order 1 for any variables which behave like du/dt = F(u), with order 2 for any variables that behave like d^2u/dt^2 = F(u), and should not call time_evolving() for any variables which behave like 0 = G(u).
Most derived systems will not have to reimplement this function; however any system which reimplements mass_residual() may have to reimplement time_evolving() to prepare data structures.
Member Data Documentation
◆ _first_order_vars
|
protectedinherited |
Variable indices for those variables that are first order in time.
Definition at line 559 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::get_first_order_vars(), libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::have_first_order_vars(), and libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::is_first_order_var().
◆ _mesh_sys
|
protectedinherited |
System from which to acquire moving mesh information
Definition at line 542 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::get_mesh_system(), libMesh::FEMSystem::mesh_position_get(), libMesh::FEMSystem::mesh_position_set(), libMesh::FEMSystem::numerical_jacobian(), and libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::set_mesh_system().
◆ _mesh_x_var
|
protectedinherited |
Variables from which to acquire moving mesh information
Definition at line 547 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::get_mesh_x_var(), libMesh::FEMSystem::mesh_position_get(), libMesh::FEMSystem::numerical_jacobian(), and libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::set_mesh_x_var().
◆ _mesh_y_var
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 547 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::get_mesh_y_var(), libMesh::FEMSystem::mesh_position_get(), libMesh::FEMSystem::numerical_jacobian(), and libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::set_mesh_y_var().
◆ _mesh_z_var
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 547 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::get_mesh_z_var(), libMesh::FEMSystem::mesh_position_get(), libMesh::FEMSystem::numerical_jacobian(), and libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::set_mesh_z_var().
◆ _second_order_dot_vars
|
protectedinherited |
If the user adds any second order variables, then we need to also cache the map to their corresponding dot variable that will be added by this TimeSolver class.
Definition at line 571 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::add_second_order_dot_vars(), and libMesh::DifferentiableSystem::get_second_order_dot_var().
◆ _second_order_vars
|
protectedinherited |
Variable indices for those variables that are second order in time.
Definition at line 564 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::get_second_order_vars(), libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::have_second_order_vars(), and libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::is_second_order_var().
◆ _time_evolving
|
protectedinherited |
Stores unsigned int to tell us which variables are evolving as first order in time (1), second order in time (2), or are not time evolving (0).
Definition at line 554 of file diff_physics.h.
Referenced by libMesh::DifferentiablePhysics::is_time_evolving().
◆ compute_internal_sides
|
inherited |
compute_internal_sides is false by default, indicating that side_* computations will only be done on boundary sides. If compute_internal_sides is true, computations will be done on sides between elements as well.
Definition at line 153 of file diff_physics.h.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following file:
generated by
